Share
Dinosaurs for Kids: Facts, Vocabulary, Games, and Coloring Pages
Step back in time with our dino-mite collection of dinosaur facts and activities for kids, including free printables!
Our all-in-one dinosaur guide is packed with fascinating dinosaur facts, simple, kid-friendly dinosaur vocabulary words, a descriptive timeline of when dinosaurs lived, free printable dinosaur coloring pages and flashcards, and educational dinosaur-themed games that make learning feel like play. You’ll also find a helpful Dinosaur FAQ section that answers kids’ most curious questions in clear, easy-to-understand language, making this a roar-some resource for parents, teachers, and dinosaur fans alike!
35+ Fun Dinosaur Facts for Kids
Dinosaur Facts by Species
Spinosaurus

Spinosaurus was one of the largest meat-eating dinosaurs. It had a long snout like a crocodile and a tall sail on its back. Scientists think it spent much of its time near water and may have hunted fish.
Tyrannosaurus rex
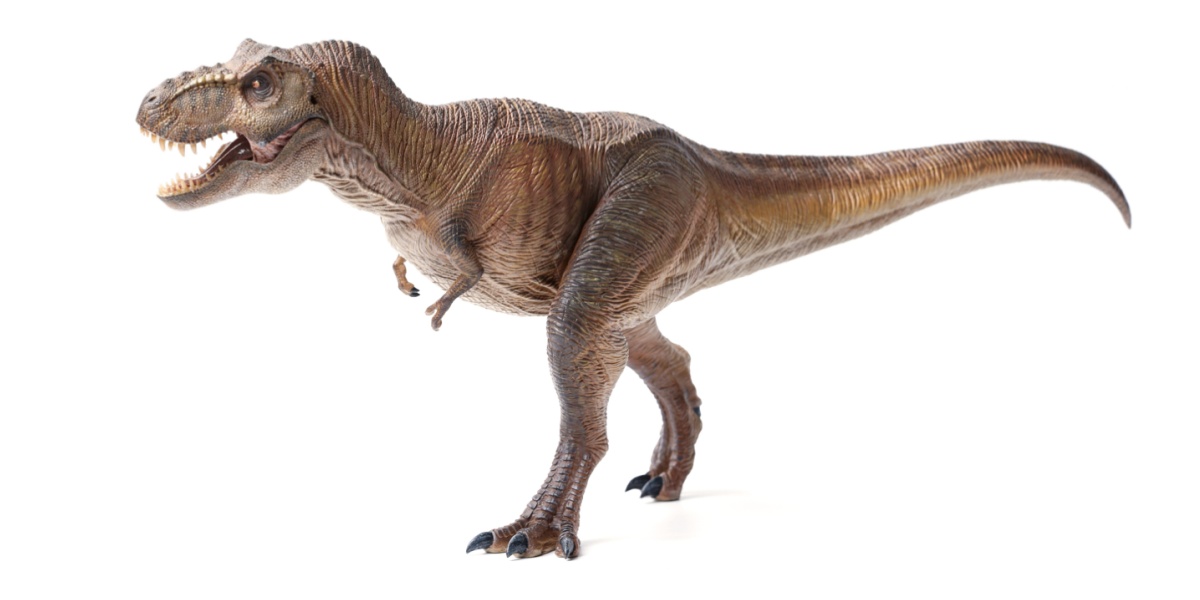

Tyrannosaurus rex, or T. rex, was one of the biggest meat-eating dinosaurs. It had huge teeth the size of bananas and powerful jaws. T. rex walked on two legs and used its sharp eyesight and strong sense of smell to find food.
Triceratops
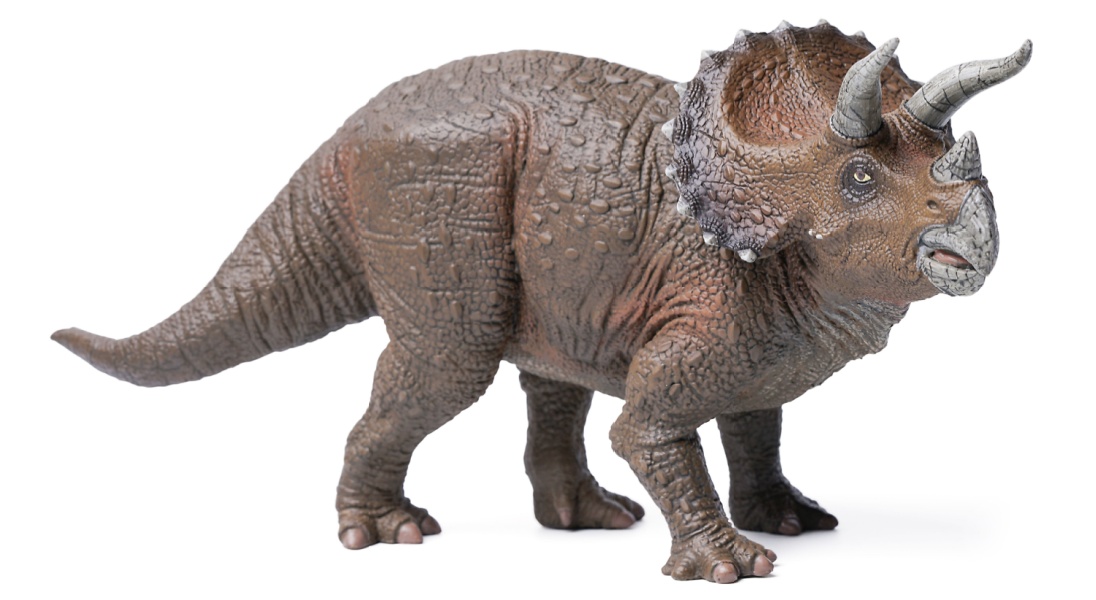

Triceratops was a plant-eating dinosaur with three horns on its face and a big frill on the back of its head. The horns helped to protect itself from predators( like T. rex). It used its beak to clip tough plants.
Stegosaurus
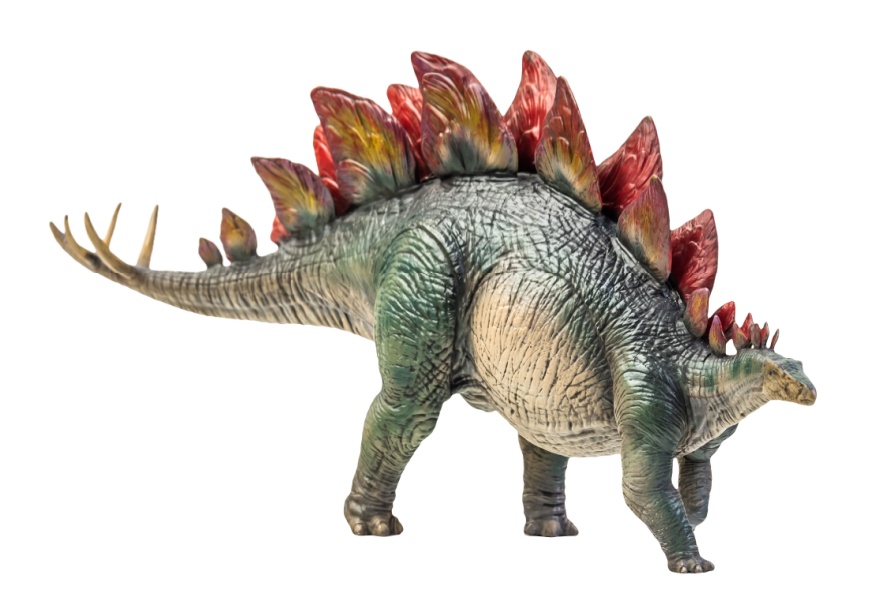

Stegosaurus was a large plant eater with big, flat plates along its back and sharp spikes on its tail. Scientists think the plates may have helped Stegosaurus stay warm or show off to other dinosaurs.
Dryosaurus
Dryosaurus was a small plant-eating dinosaur that could run very fast, which helped it escape large meat-eating predators. Its name means “oak lizard,” but it did not actually eat oak trees. Dryosaurus had a long, stiff tail that helped it keep its balance while running. Scientists think it may have lived in groups, which could have offered extra protection from predators.
Hypsilophodon
Hypsilophodon was a small, lightweight dinosaur, about the size of a large dog. It had a beak-like mouth that helped it bite and chew plants. This dinosaur ran on two legs, allowing it to move quickly when danger was nearby. Hypsilophodon lived during the Early Cretaceous period, more than 125 million years ago.
Brachiosaurus

Brachiosaurus was a giant, long-necked dinosaur that ate leaves from tall trees. Its front legs were longer than its back legs, which helped it reach high branches. It was one of the tallest dinosaurs ever found.
Apatosaurus
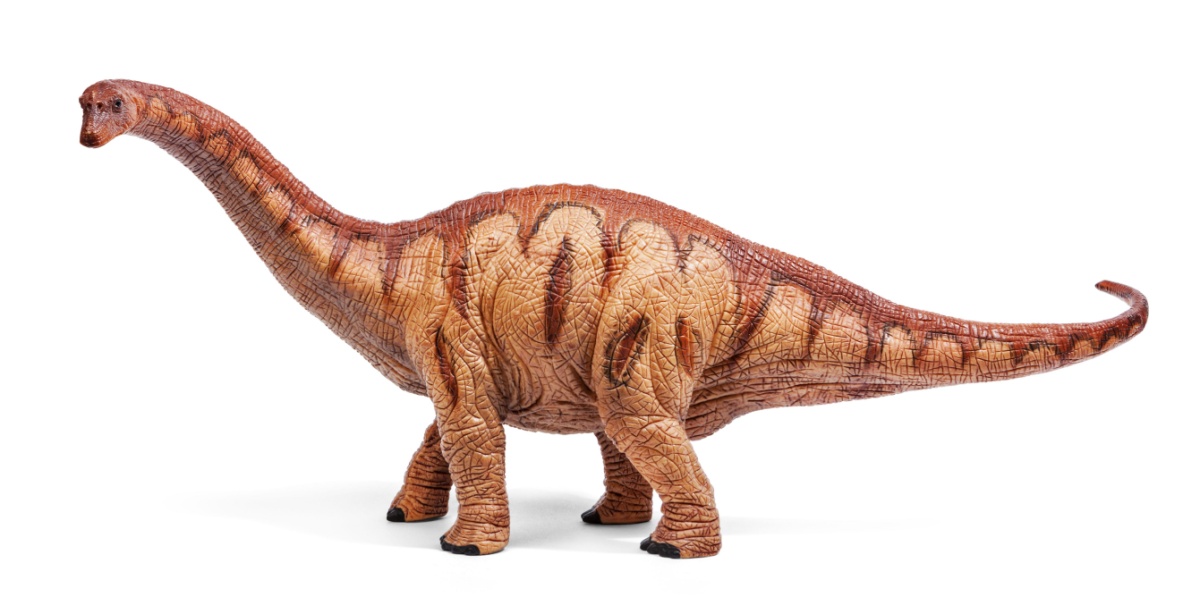

Apatosaurus was a massive long-necked dinosaur that ate plants. It had a long tail that may have made a loud cracking sound when whipped. Apatosaurus spent much of its time eating leaves and ferns. It weighed up to 40 tons and was up to 75 feet long!
Diplodocus
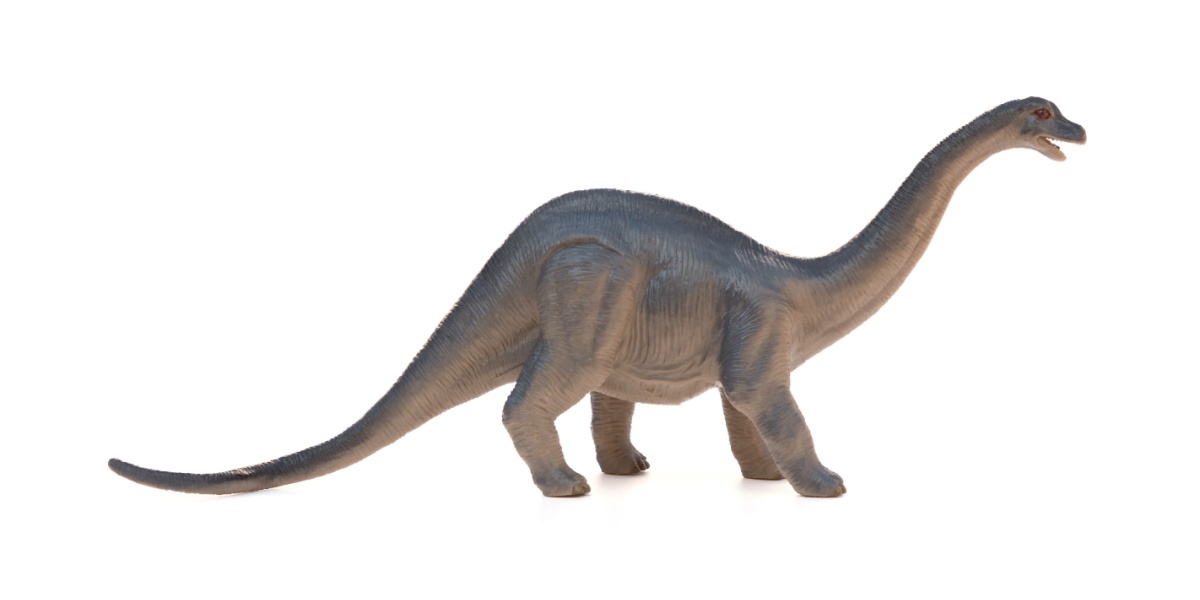

Diplodocus was a very long dinosaur with a whip-like tail. It used its long neck to reach lots of plants without moving much. Its teeth were shaped like pegs, perfect for stripping leaves.
Ankylosaurus
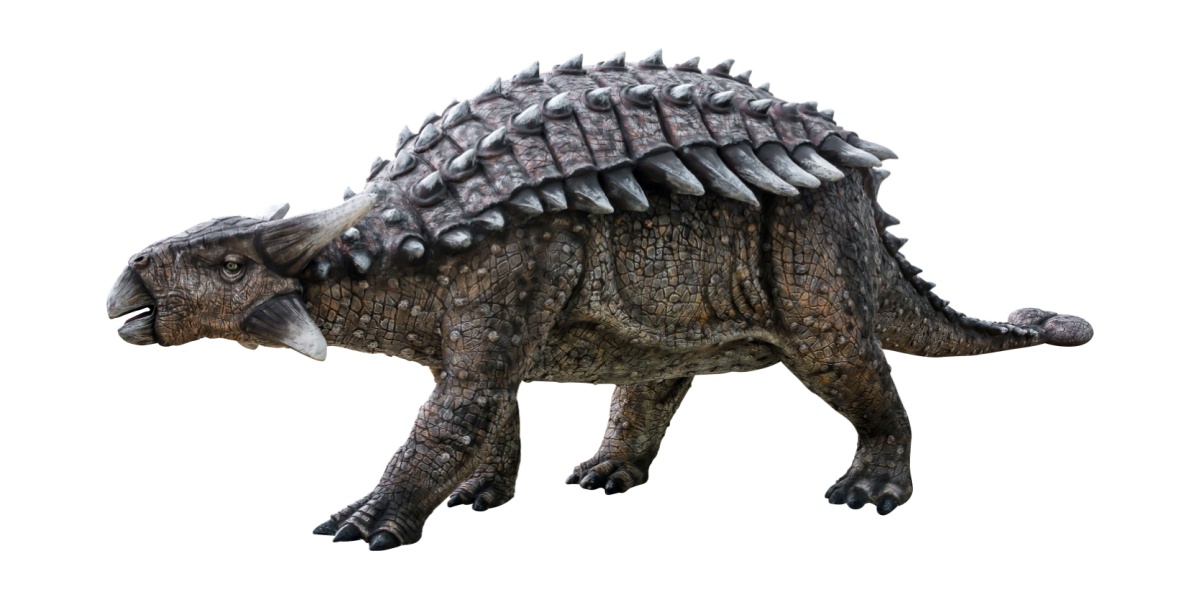

Ankylosaurus was a heavily armored dinosaur covered in bony plates. It had a large club at the end of its tail that it used for protection. It ate low-growing plants.
Allosaurus
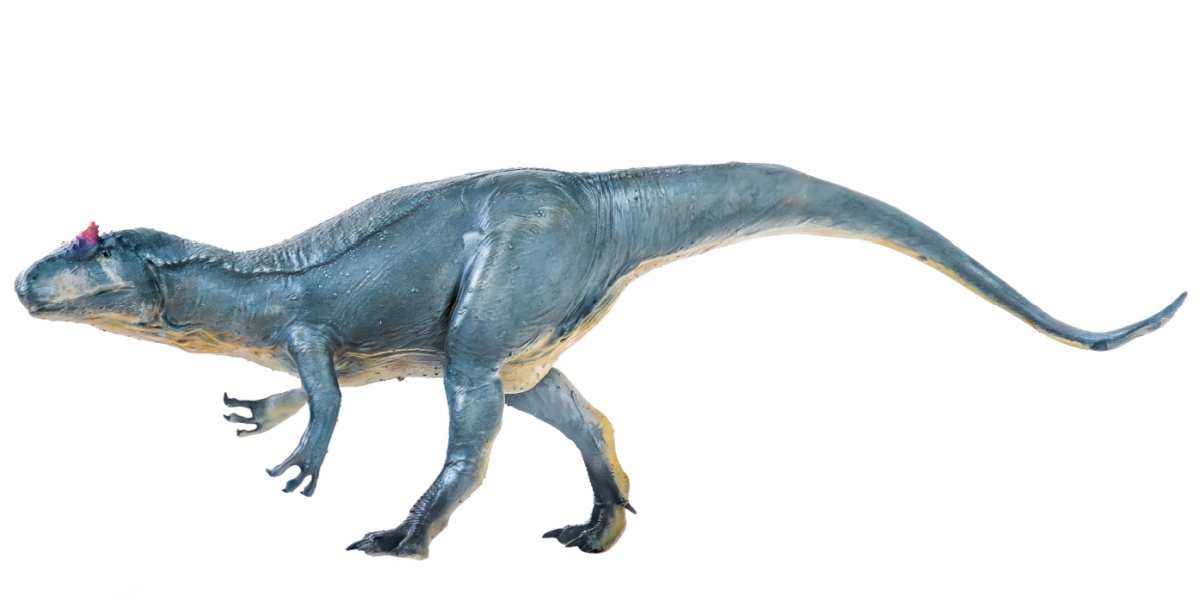

Allosaurus was a large predator that lived long before T. rex. It had sharp teeth and claws and hunted in forests and plains. Some scientists think Allosaurus may have worked together to take down big prey.
Parasaurolophus
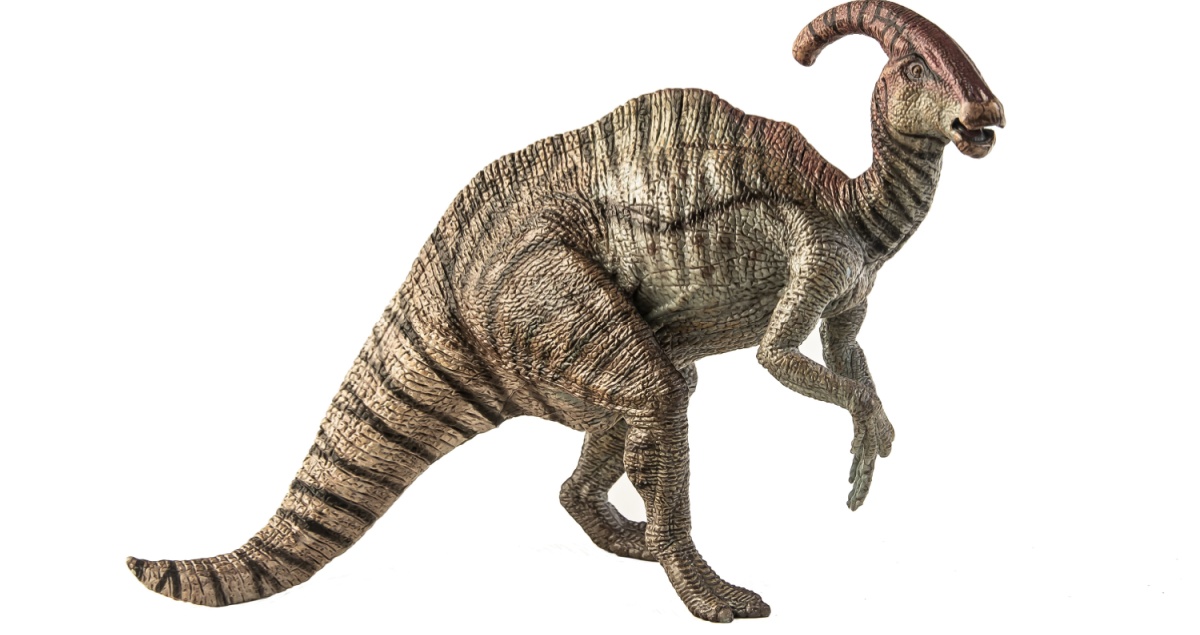

Parasaurolophus was a plant-eating dinosaur with a long, curved crest on its head. Scientists think the crest helped it make loud, trumpet-like sounds to communicate with other dinosaurs.
Lesothosaurus
Lesothosaurus was one of the earliest known plant-eating dinosaurs. It was small, measuring about the length of a bicycle from head to tail. This dinosaur likely fed on low-growing plants and leaves close to the ground. Its long legs suggest it could run quickly to escape predators.
Scutellosaurus
Scutellosaurus was a small dinosaur covered with tiny bony plates, which helped protect its body. It is considered one of the earliest armored dinosaurs known to science. Even with its armor, Scutellosaurus remained lightweight and able to move quickly. It lived during the Early Jurassic period, over 190 million years ago.
Pachycephalosaurus
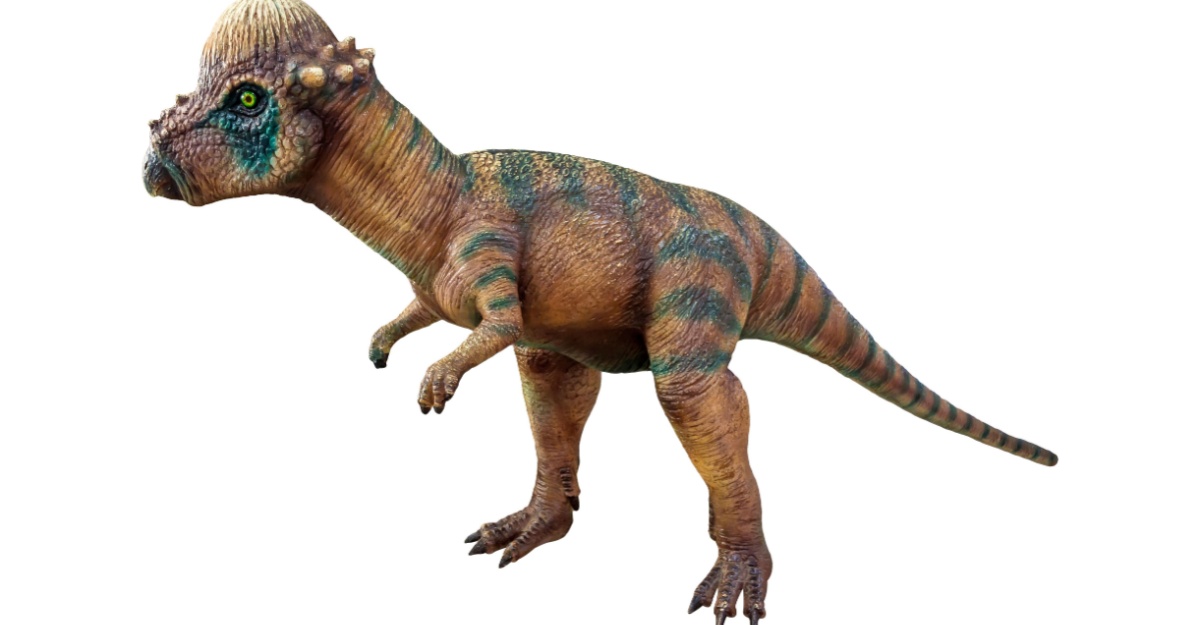

Pachycephalosaurus had a thick, domed skull that could be up to 10 inches (25 cm) thick. It may have used its hard head to bump into other dinosaurs of its kind. It ate plants and maybe fruits.
Iguanodon
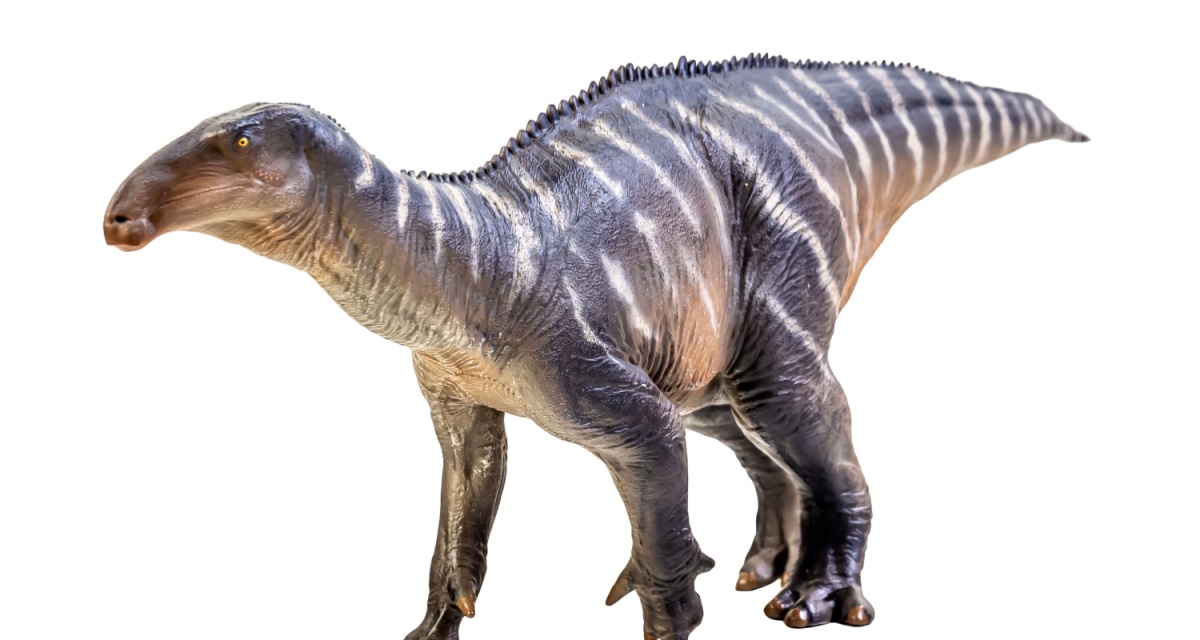

Iguanodon was a plant-eating dinosaur with a large thumb spike. The spike may have been used for defense. It walked on two or four legs and had strong jaws for chewing plants.
Heterodontosaurus
Heterodontosaurus had three different kinds of teeth, making it one of the most unusual dinosaurs of its time. Its sharp, canine-like teeth were likely used for display or defense, not for hunting other animals. This dinosaur mostly ate plants, but scientists think it may have also eaten insects. It was very small, about the size of a turkey.
Leaellynasaura
Leaellynasaura lived near the South Pole, where it experienced long periods of darkness each year. Scientists believe it had relatively large eyes, which may have helped it see in low-light conditions. This dinosaur survived in a cool, polar climate, unlike many other dinosaurs. It fed on tough plants and ferns that grew in its environment.
Giganotosaurus
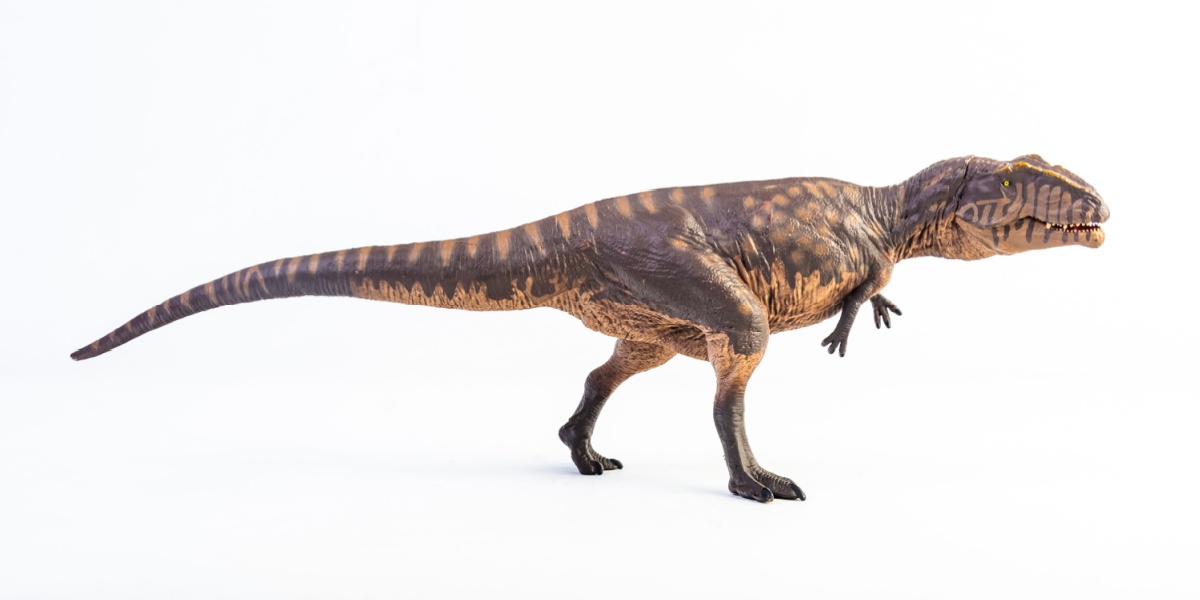

Giganotosaurus was one of the longest meat-eating dinosaurs, even longer than T. rex. It had long, sharp teeth and hunted large plant-eating dinosaurs in groups or alone.
Carnotaurus
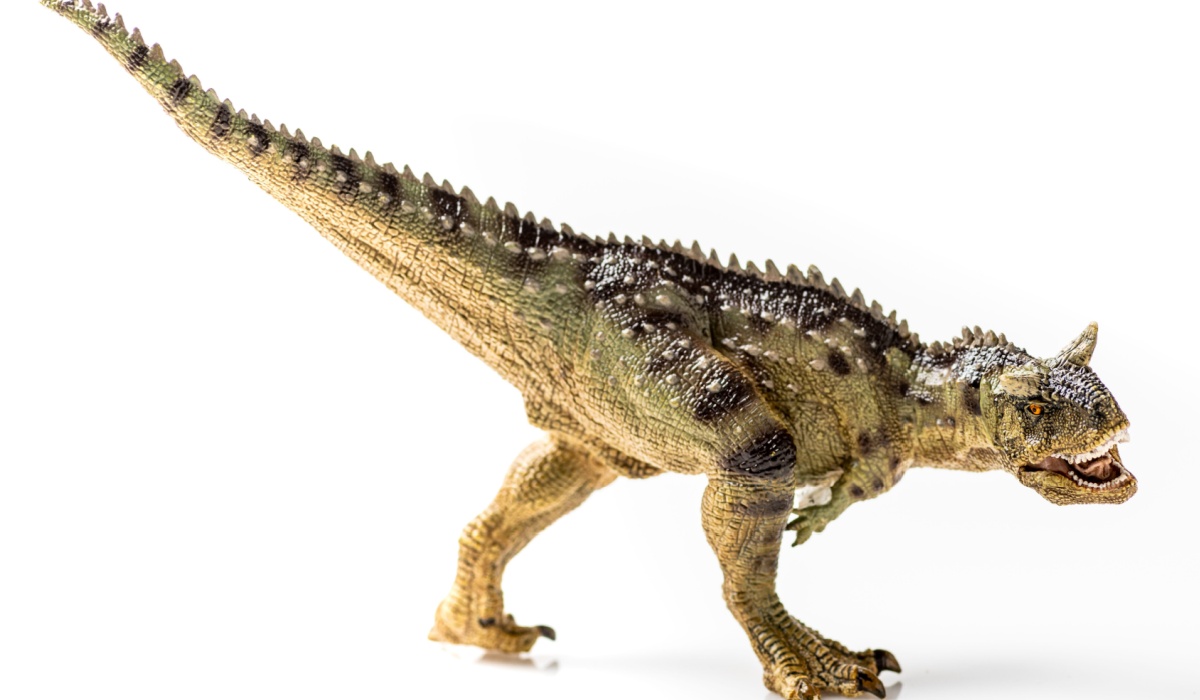

Carnotaurus was a fast meat-eating dinosaur with two short horns above its eyes. It had tiny arms—smaller than T. rex’s!—and a long, powerful tail that helped it move quickly.
More Dinosaur Facts for Kids
- Dinosaurs lived millions of years ago, long before humans appeared.
- Some dinosaurs were as small as chickens, while others were longer than school buses.
- Not all dinosaurs were meat eaters—many loved plants, leaves, and ferns.
- Some dinosaurs, like Velociraptor, had feathers.
- Triceratops had three horns that helped protect it from predators.
- Stegosaurus had a tiny brain—about the size of a lime!

- The word “dinosaur” means “terrible lizard,” even though dinosaurs weren’t lizards.
- Many dinosaurs laid eggs, and some even cared for their young.
- Some dinosaurs, like Allosaurus, ran on two legs, while others, like Brachiosaurus, walked on four.
- Birds are actually modern dinosaurs that evolved from small, feathered theropods.
- Some dinosaurs lived in herds, traveling together for safety and food.
- Sauropods such as Argentinosaurus were the largest land animals to ever live.
- Fossils show that many dinosaurs grew quickly, especially when they were young.
- Some small dinosaurs, like Ornithomimus, were very fast and may have run up to 40 miles per hour.
- Dinosaurs lived during the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods, which together are called the Mesozoic Era.
- Many dinosaurs had special features—like crests, sails, or frills—that helped them communicate, show off, or defend themselves.
- Paleontologists use fossils such as bones, teeth, footprints, and even eggs to learn how dinosaurs lived.
Dinosaur Vocabulary Words for Kids
Learning about dinosaurs is more fun when you understand the words use to describe them. This dinosaur vocabulary list explains common dinosaur terms in simple language, so kids can better understand the language that learn what the words mean while exploring dinosaur
Dinosaur Group Names
These words describe types of dinosaurs, based on body shape and diet.
- Sauropod – A very large, long-necked plant-eating dinosaur, like Brachiosaurus.
- Theropod – A two-legged dinosaur that usually ate meat, like T. rex.
- Ornithischian – A group of mostly plant-eating dinosaurs with bird-like hips.
- Saurischian – A group that includes theropods and sauropods with lizard-like hips.

- Armored dinosaur – A dinosaur with bony plates or spikes for protection.
- Hadrosaurs – Plant-eating dinosaurs with wide, flat “duck-bill” mouths, like Parasaurolophus.
- Ceratopsians – Plant-eating dinosaurs with horns and frills on their heads, like Triceratops.

Dinosaur Science Words
These words are often used by scientists and paleontologists.
- Fossil – The remains or prints of a plant or animal from long ago.
- Paleontologist – A scientist who studies fossils.
- Excavation – Carefully digging to find fossils.
- Extinction – When a plant or animal disappears forever.
- Species – A group of animals that are alike and share a name.
Dinosaur Body Part Words
These words describe how dinosaurs looked and parts of their bodies that helped distinguish them from other dinosaurs.
- Crest – A bony shape on a dinosaur’s head.
- Frill – A large bony shield behind the head, like on Triceratops.
- Plates – Flat bony armor on a dinosaur’s back.

- Tail – Helped with balance and movement.
- Claws – Sharp nails used for gripping or defense.
- Sail – A tall, thin structure on a dinosaur’s back made of bone and skin, often used for display or warmth.

Dinosaur Diet Words
These words explain what dinosaurs ate.
- Herbivore – A plant-eating dinosaur.
- Carnivore – A meat-eating dinosaur.
- Omnivore – A dinosaur that ate both plants and animals.
- Prey – An animal that is hunted by another.
- Predator – An animal that hunts other animals.

Dinosaur Timeline: When Did Dinosaurs Live?
Dinosaurs lived on Earth for a very long time—over 165 million years. They first appeared long before humans and disappeared millions of years before people existed. The long time period when dinosaurs ruled Earth is known as the Mesozoic Era.
Scientists divide dinosaur time into three main periods, based on fossil evidence.
🦕 The Triassic Period (About 252–201 Million Years Ago)
🦕 The Jurassic Period (About 201–145 Million Years Ago)
🦕 The Cretaceous Period (About 145–66 Million Years Ago)

What is the Triassic Period?
The Triassic Period is when the very first dinosaurs appeared. Early dinosaurs were small, lightweight, and walked on two legs. Earth looked very different back then, with most land joined together in one giant continent called Pangaea. The Triassic ended with a major extinction event that cleared the way for dinosaurs to become the dominant land animals in the Jurassic Period.
During this time:
- The climate was hot and dry in many places.
- Plants such as ferns, conifers, and ginkgo trees were common.
- Early dinosaurs like Coelophysis and Plateosaurus lived during this time, along with many strange reptiles and the first mammals.
- Dinosaurs were not yet the dominant animals, and many reptiles and early mammals also lived on Earth.
What is the Jurassic Period?
The Jurassic Period is when dinosaurs became the largest and most powerful animals on land. This was the age of giant long-necked dinosaurs like Brachiosaurus and Diplodocus, spiky dinosaurs like Stegosaurus, and fast hunters like Allosaurus.
During this time:
- Flying reptiles called pterosaurs filled the skies (they were not dinosaurs).
- The Earth was warm, and huge green forests covered much of the land.
- Dinosaurs grew much bigger and some began to develop feathers
What is the Cretaceous Period?
The Cretaceous Period was the final age of dinosaurs. During this time, dinosaurs were found all over the world and were more diverse than ever, with many different shapes, sizes, and diets. The Cretaceous Period ended with a massive asteroid impact that caused a huge extinction event, bringing the time of the dinosaurs to a close and allowing mammals to rise in the eras that followed.
During this time:
- Flowering plants appeared for the first time, changing how dinosaurs ate and making Earth greener and more colorful.
- Many well-known species, like Tyrannosaurus rex, Triceratops, Velociraptor, and Spinosaurus, lived during this period.
- The continents were moving apart and starting to look more like they do today.
- Some dinosaurs lived in cold or polar regions.
- Birds evolved from feathered dinosaurs.
Free Dinosaur Printables
Dinosaur Coloring Pages

List of 100 Dino Names

Dinosaur Flash Cards

Dinosaur Jokes

COMING SOON!
Educational Dinosaur-Themed Games for Kids
Combine dinosaurs with play-based learning to make practicing math, literacy, and science totally roar-some! Click on the name of each dinosaur game to play it for free.

Draco’s Dash: Odd Numbers
Help Draco race through jungle by running through the odd numbers and avoiding the even number!

Dinosaur Chomp
This hungry dino needs to eat the leaves with the correct number of rain drops on them. Can you pick the right ones?

Fossil Finder
Take on the role of paleontologist in this game that lets kids “dig” up fossils and test their knowledge about what they find.

Nutly’s Dinosaur Daydreams
Nutly is daydreaming about dinosaurs but needs help completing his thoughts. You’ll need to pick the correct noun, adjective, or verb to finish his sentences.

D is for Dinosaur: Online Coloring Page
In this digital coloring page, kids can color a dinosaur while learning the letter /d/ sound and letter D recognition.

Dracos Dash: Letters A through D
Dash with Draco the dinosaur as he collects the letters A through D! Help him jump for the right ones and dodge the rest in this fun letter learning game.
Dinosaur FAQs
What is a dinosaur?
A dinosaur is an animal that lived on land during the Mesozoic Era, between about 230 and 66 million years ago. Dinosaurs had legs that stood upright under their bodies, which helped them walk and run efficiently. Some dinosaurs ate plants, some ate meat, and some ate both. Birds are the only dinosaurs still alive today.
When did dinosaurs live?
Dinosaurs lived during the Mesozoic Era, which lasted from about 230 to 66 million years ago. This era is divided into three periods: the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous. Different dinosaurs lived during different periods, and new species evolved over time.
Why did dinosaurs go extinct?
Most dinosaurs went extinct about 66 million years ago after a large asteroid struck Earth. The impact caused major climate changes by blocking sunlight and cooling the planet. Plants could not grow, and food chains collapsed. Many animals, including non-bird dinosaurs, could not survive these changes. Birds survived and are living dinosaurs today.
Are dinosaurs still alive today?
Yes, dinosaurs are still alive today in the form of birds. Scientists have discovered that birds evolved from small, feathered dinosaurs. Birds share many features with dinosaurs, including hollow bones and similar skeletons. All other dinosaur groups went extinct millions of years ago.
What is the biggest dinosaur ever discovered?
The biggest dinosaurs ever discovered were sauropods, long-necked plant-eaters like Argentinosaurus. These dinosaurs could grow over 100 feet long and weigh many tons. Because fossils are often incomplete, scientists continue to study new discoveries to better understand their size.
How big was T. rex?
Tyrannosaurus rex was one of the largest meat-eating dinosaurs ever discovered. It grew to about 40 feet (12 meters) long and stood about 12 feet (3.6 meters) tall at the hips. Scientists estimate that T. rex weighed around 8 to 9 tons, which is about as much as a large truck.
Did all dinosaurs eat meat?
No, not all dinosaurs ate meat. Many dinosaurs were herbivores, meaning they ate plants, while others were carnivores that ate meat. Some dinosaurs were omnivores and ate both plants and animals. A dinosaur’s teeth and jaw shape help scientists understand what it ate.
How do scientists know what dinosaurs looked like?
Scientists study fossil bones, compare them to modern animals, and use computer models to understand how dinosaurs moved and lived. Some fossils show skin impressions or feathers, helping scientists make accurate reconstructions. New discoveries often update what we know about dinosaur appearance.
What is a fossil?
A fossil is the preserved remains or traces of a plant or animal that lived long ago. Dinosaur fossils can include bones, teeth, footprints, or even nests. Fossils form when living things are buried by sediment and slowly turn into rock over millions of years.
How do you explain dinosaurs to a child?
Dinosaurs were animals that lived on Earth millions of years ago, long before people existed. They lived during a time called the Mesozoic Era, which is often called the Age of Dinosaurs. Some dinosaurs were very large, while others were small. We learn about dinosaurs by studying fossils, which are their remains preserved in rock.