Share
Online Game-Based Learning: Why It Works
Research suggests that online learning games help children increase early math and literacy skills, cognitive development, and critical thinking. Here’s how your child can benefit.
Table of Contents–Jump to Each Section
In the preschool and early elementary years, children absorb knowledge rapidly—making this a critical time to build early math, literacy, cognitive, and social-emotional skills. Research shows that online learning games can boost this development through fun, interactive experiences.
For example, when reporting on the impact of educational apps on learning, a 2024 article published in the journal Children found that “By integrating educational content with game mechanics, these apps can make learning more enjoyable and effective, leading to better retention and understanding of complex concepts.”
“By integrating educational content with game mechanics, these apps can make learning more enjoyable and effective, leading to better retention and understanding of complex concepts.” –Clemente-Suárez et al. Children. 2024; 11(11):1299
Studies also suggest that online educational games can promote problem-solving and critical thinking and improve engagement and motivation, adding to their value as a learning resource for children.
Explore the research highlighting how online learning games and interactive educational apps contribute to early childhood development and a simply way to add game-based learning to your home or classroom.
What Is Game-Based Learning?

Game-based learning, which includes online games, board games, card games, and more, integrates educational content into interactive games designed to help players develop, build, and practice their skills. Experts carefully craft these games to teach specific concepts or knowledge through play — a proven method for actively engaging young learners. Online learning games are a popular example of game-based learning, offering interactive experiences that make practicing skills more fun and effective.
Examples of game-based learning:
- Vocabulary word crossword puzzle
- Math facts Bingo game
- Science trivia Jeopardy
- Online skip counting game
In each of these activities, students learn or practice knowledge and skills with a clear learning objective in mind. The games are interactive and even strategic, adding a playful element that actively engages students in the learning process.
Game-based learning is especially effective for younger children. According to research presented in Frontiers in Psychology, “…game-based learning can be a promising tool for early childhood educators to promote children’s learning and development…Researchers and educators recognized the potential of game-based learning to enhance engagement, motivation, and learning outcomes in early childhood education.”
Game-Based Learning vs. Gamification
It’s important to note that game-based learning is different from gamification, another commonly used term. Gamification adds game-like elements into more traditional teaching methods, such as rewarding students with a small prize for answering a question correctly during a lesson. These game elements help increase engagement and motivation, but they don’t have an educational objective on their own.
In game-based learning, the game is the lesson. After students play the game, they have a deeper understanding of the content or demonstrate better mastery of a skill.
In game-based learning, the game is the lesson. After students play the game, they have a deeper understanding of the content or demonstrate better mastery of a skill. They might receive rewards like prizes, tickets, badges, or points, but learning is the overall objective of the game itself.
Literacy Skills Improve with Online Learning Games
While it’s been established that digital learning apps and games can improve students’ engagement, studies reveal that they can also have a measurable impact on literacy skills.
In a 2025 study published in the journal Learning and Individual Differences, researchers found that playing apps specifically designed for teaching literacy for just 30 minutes per week increased preschoolers’ reading skills. This was true regardless of the child’s family background, income, or existing literacy skills before playing the online learning games.
Researchers found that playing apps specifically designed for teaching literacy for just 30 minutes per week increased preschoolers’ reading skills.
Specifically, these apps were beneficial in teaching the early literacy skills preschool children need to develop, such as letter recognition, phonological awareness, letter-sound correspondence, and letter tracing.
The authors noted, “Our findings show that our educational game-based literacy apps can act as additional means to support young children from all backgrounds in the acquisition of their early literacy skills. This kind of educational literacy apps (sic) offers parents with little financial, educational, or time resources the chance to support their children meaningfully.”
Math Skills Improve with Online Learning Games

Research also captures the high value of online game-based learning for teaching early math skills like number recognition, counting, addition, and subtraction. Digital math games help kids master new concepts and develop and strengthen problem-solving skills in general.
A study published in the February 2025 volume of the International Journal of Learning, Teaching and Educational Research examined the immediate and long-term benefits of playing online math games. The researchers found that the second graders in this study who played online math games outperformed their peers in post-tests designed to measure both immediate and long-term recall and application of skills.
“This suggests that DGBL (digital game-based learning) is not only effective in helping students grasp mathematical concepts in the short term but also in strengthening their ability to retain and apply these concepts over time,” the authors wrote.
We also know that motivation plays a crucial role in math performance. Digital game-based learning increases student engagement by turning number and math mastery into an enjoyable activity. In a review of 35 studies published in Frontiers of Psychology in 2023, researchers concluded that while math is “often considered to be a difficult or boring subject,” online learning games can increase engagement and motivation.
“Game-based learning elements that emphasize competition and learning while playing make the learning more enjoyable for the students and reduces their anxiety about math subjects.” –Hii, B. H., & Mahmud, M. S. (2023). Frontiers in Psychology, 14, Article 1105806
Cognitive Benefits of Game-Based Learning

Along with improving literacy and numeracy skills for children, digital game-based learning also positively impacts cognitive development.
According to studies, interactive, goal-oriented games can improve memory, focus, problem-solving, and cognitive flexibility by engaging children in fun, challenging tasks.
How Online Learning Games Help Improve Cognitive Development:
Boost memory and recall by encouraging children to remember patterns, sequences, and information in context.
Improve attention and concentration through fast-paced, engaging tasks that require focus and quick thinking.
Enhance problem-solving and cognitive flexibility by challenging kids to make decisions, solve puzzles, and adapt to new situations.
Increase motivation and engagement with rewards, feedback, and interactive experiences that make learning enjoyable.
Support executive functioning by strengthening skills like planning, organizing, and managing emotions during gameplay.
See the research supporting the positive impact of online learning games on children’s cognitive development.
Boost Social and Emotional Growth with Online Game Play

While early childhood is a time of rapid cognitive growth, it’s also an ideal time to nurture social-emotional learning (SEL) skills, and research shows that online learning games can help their development.
Interactive games offer safe, engaging spaces where kids can practice managing emotions, building confidence, working with others, and making thoughtful decisions. When used alongside everyday social experiences, game-based learning provides another valuable way to support a child’s emotional and social growth.
How Online Learning Games Help Kids Grow Social-Emotional Skills:
Improve emotional regulation by helping children recognize and manage their feelings during gameplay
Build resilience and self-confidence through risk-taking, persistence, and learning from mistakes
Boost motivation and goal setting with fun challenges, rewards, and progress tracking
Encourage communication and teamwork in multiplayer or cooperative games
Strengthen decision-making and problem-solving by requiring critical and strategic thinking
See an overview of the studies showcasing the social-emotional growth that can occur with online learning games.
Add Game-Based Learning to Your Child’s Routine

The ABCmouse learning app puts the benefits of game-based learning into action for children from preschool to second grade (ages 2-8), focusing on the development of literacy, math, social studies, science, art, and music skills.
In a 2025 study, researchers found that using ABCmouse can double early learning gains in both reading and math. Among the key findings:
- Pre-kindergarten children who used ABCmouse for about 3.5 months demonstrated 2.5 times greater growth in their phonological processing skills in comparison to their peers who did not use the program.
- Children who used ABCmouse also demonstrated 1.6 to 2 times greater growth in their quantitative reasoning and applied math problem-solving skills relative to their peers who did not use the program.
The recent study’s results underscored findings from earlier research. In 2016, ABCmouse was shown to improve kindergarten readiness for Head Start students, with authors noting, “for every additional 100 ABCmouse learning activities completed by a student, there is a 3.6% boost in school readiness scores from the beginning to the end of the school year.”
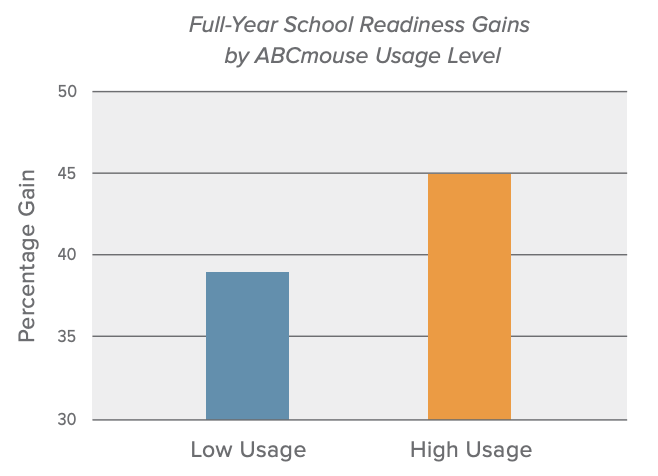
In 2019, another ABCmouse study found that children who used the program’s online learning curriculum over the summer months avoided the notorious “summer slide” learning loss. Even more, these students returned to school in the fall demonstrating academic gains equivalent to an additional month of instruction compared to their peers.
“Programs such as … and ABCmouse utilizes adaptive learning techniques to keep students focused on tasks that are appropriately challenging, thus enhancing their ability to sustain attention over extended periods. These tools provide immediate feedback and rewards, which can motivate students to stay attentive and improve their focus.”
ABCmouse was specifically called out in a 2023 article in the journal Children, where the authors stated, “Programs such as … and ABCmouse utilizes adaptive learning techniques to keep students focused on tasks that are appropriately challenging, thus enhancing their ability to sustain attention over extended periods. These tools provide immediate feedback and rewards, which can motivate students to stay attentive and improve their focus.”
Evidence suggests that adding online learning games to a teacher’s or parent’s toolkit brings benefits for children, especially when blended into a comprehensive curriculum or used to supplement the lessons, activities, reading, and worksheets that often come with more traditional learning.
Ready to Try Game-Based Learning?
Explore ABCmouse’s full library of educational games and start supporting your child’s learning through play today.

Game-Based Learning FAQs
What is game-based learning?
Game-based learning involves mixing educational content into interactive games. In this approach, experts carefully design games to help players build, grow, and practice specific skills. Learning through play gives children a fun and proven way to pick up specific skills, concepts, or knowledge.
Are online learning games good for early childhood development?
Online game-based learning is very effective for young children. At this age, learning through play feels natural since play is how young children explore and understand the world around them. Games provide a safe space for kids to try new concepts, make mistakes, and try again. Engaging game features also help hold kids’ attention and provide multiple paths to learning.
Does research support the use of digital game-based learning apps?
Multiple peer-reviewed studies in recent years have shown that digital game-based learning can be a great way to boost cognitive development by engaging players in fun, challenging activities that help improve memory, attention, problem-solving, and mental flexibility. It can also increase engagement, motivation, and knowledge around specific skills, such as literacy and math, making it a valuable tool for both education and personal growth.
What skills do online games teach preschoolers?
In addition to supporting cognitive development and social-emotional learning, online learning games can teach the foundational math and literacy skills children need at this age. Players may learn letter and number recognition, phonological awareness, letter-sound correspondence, counting, basic addition and subtraction, and much more.
Do online learning games support social-emotional learning (SEL)?
Research shows that interactive online learning apps can promote SEL skills like resilience, emotional regulation, self-confidence, motivation, collaboration, and time management. These skills are often an inherent part of game-based learning, regardless of whether games are specifically designed to teach these specific SEL concepts.
How can I help my child learn with educational games?
ABCmouse games are designed to foster development in literacy, math, social studies, science, art, and music for kids ages 2 to 8. By spending just a few minutes each day using online learning games like these, your child will develop cognitive and academic skills in a fun, challenging environment. The digital game-based learning aspect motivates them, keeping them engaged to fostering a love of learning itself.
Legal disclaimer: Any information, materials, or links to third-party resources are provided for informational purposes only. We are not affiliated with and do not sponsor/endorse these third parties and bear no responsibility for the accuracy of content on any external site. All information provided in this article is current as of May 2025.
References:
Clemente-Suárez VJ, Beltrán-Velasco AI, Herrero-Roldán S, Rodriguez-Besteiro S, Martínez-Guardado I, Martín-Rodríguez A, Tornero-Aguilera JF. Digital Device Usage and Childhood Cognitive Development: Exploring Effects on Cognitive Abilities. Children (Basel). 2024 Oct 27;11(11):1299. doi: 10.3390/children11111299. PMID: 39594874; PMCID: PMC11592547.
Alotaibi MS (2024) Game-based learning in early childhood education: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychol. 15:1307881. Doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1307881
Youling Li, Di Chen, and Xinxia Deng, “The Impact of Digital Educational Games on Student’s Motivation for Learning: The Mediating Effect of Learning Engagement and the Moderating Effect of the Digital Environment,” PLOS ONE 19, no. 1 (2024): e0294350, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0294350.
Schiele, T., Edelsbrunner, P., Mues, A., Birtwistle, E., Wirth, A., & Niklas, F. (2025). The effectiveness of game-based literacy app learning in preschool children from diverse backgrounds. Learning and Individual Differences, 117, 102579. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1041608024001729
Al-Hassan, O. M., Alhasan, L. M., AlAli, R. M., Al-Barakat, A. A., Al-Saud, K. M., & Ibrahim, N. A. (2025). Enhancing early childhood mathematics skills learning through digital game-based learning. International Journal of Learning, Teaching and Educational Research, 24(2), 141–160. https://doi.org/10.26803/ijlter.24.2.10
Hii, B. H., & Mahmud, M. S. (2023). Influence of game-based learning in mathematics education on the students’ cognitive and affective domain: A systematic review. Frontiers in Psychology, 14, Article 1105806. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1105806